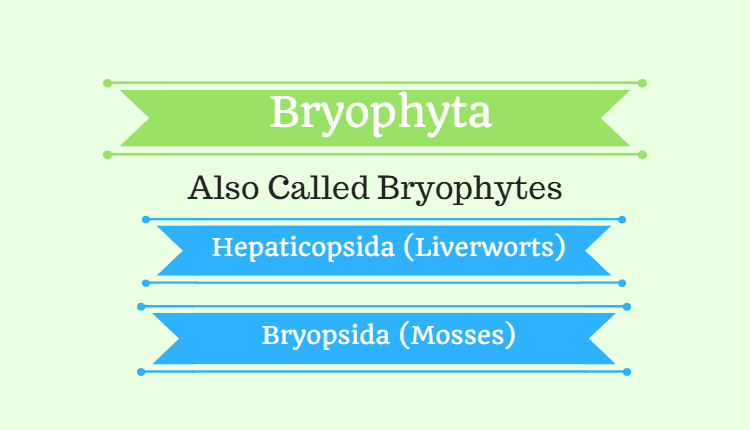
Bryophyta (Bryophytes)
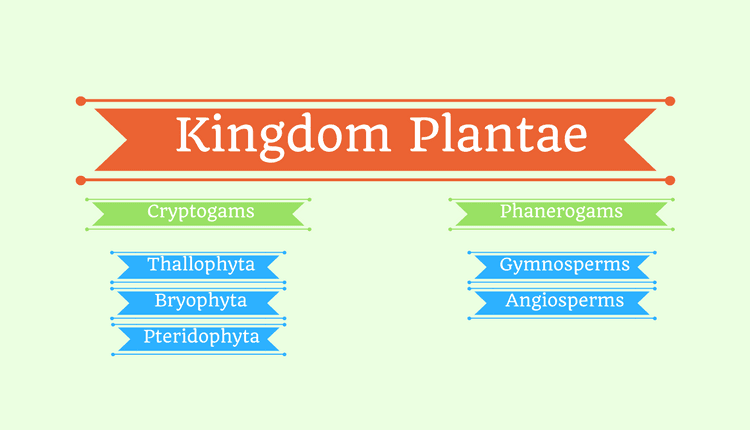
The Kingdom Plantae was divided into two sub kingdoms depending on whether they can form seeds or not. The two sub kingdoms were cryptogams and phanerogams. Cryptogams included the primitive plants such as thallophytes, bryophytes, and pteridophytes while phanerogams included gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Bryophytes are small, undifferentiated, non-vascular plants. These include mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. These grow in moist and damp habitats in the form of mats or cushions over rocks and soils and even on trunks and leaves of trees as epiphytes. These are also called amphibians of the plant kingdom.
General Characteristics of Bryophytes
- The plant body is not differentiated into root, stem, and leaves.
- The life cycle consists of two stages sporophytic and gametophytic stage. This is called alternation of generation.
- Vascular system (xylem and phloem tissues) is absent.
- Plants are gametophytic and green in color due to the presence of chlorophyll.
- The sporophytic phase is short lived and produces haploid spores.
- The plant has root like structure called rhizoids for Anchorage. Rhizoids can be unicellular and multicellular.
Reproduction in Bryophytes
- Reproduction in bryophytes is oogamous type i.e. the female gamete is large and non-motile and male gamete is small and motile.
- The male reproductive organs are antheridia (singular – antheridium) and the female reproductive organs are archegonia (singular – archegonium).
- Antheridia have a cylindrical or elongated body with a long or short stalk. These contain androgonial cells or androcytes or antherozoid mother cells that give rise to a single motile
- Archegonia are flask shaped with swollen base known as venter and a long elongated neck. Each archegonium consists of a large egg, numerous neck canal cells, and a ventral canal cell.
- Reproductive organs are surrounded by a single layer of the sterile
- Motile antherozoids, when released from the mature archegonium, swim in water and reach the neck of archegonium where fertilization takes place. A zygote is formed that divides continuously to form a multicellular embryo.
- Embryo then differentiates into a new sporophyte.
- The body of sporophyte is divided into the foot, seta, and capsule. The capsule is present on the top and connected to the foot with a seta. The capsule contains archesporium that contains archesporial cells. These give rise to spore mother cells that produce four haploid spores by meiosis.
- Each spore forms a new gametophyte.
Classification of Bryophytes
Bryophytes are further divided into two different classes:
- Hepaticopsida (Liverworts)
- Bryopsida (Mosses)
Economic Importance of Bryophytes
Bryophytes are both ecologically and economically important. Some of the economic importance of bryophytes is as follows:
- Sphagnum, a bryophyte is used to produce peat moss. Peat moss is harvested and dried and used as fuel. This bryophyte is also used in horticulture for packing plants during transportation.
- These can be used as bioindicators of pollution.
- These are the first species to colonize a place and make the habitat suitable for other organisms to grow.
- These have water holding capacity thus maintain the moisture in the soil.
- These also recycle nutrients in the forest.