Temperate Forests
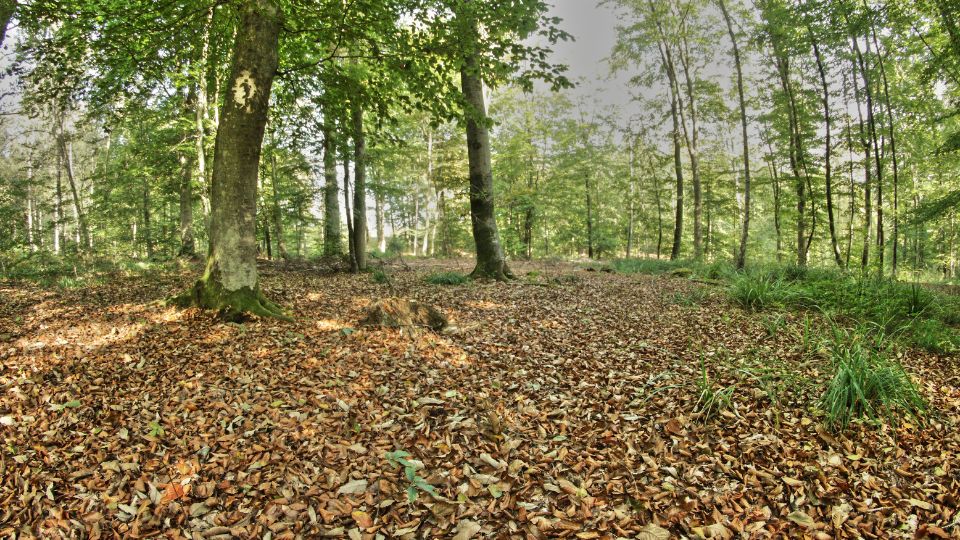

Temperate forests are a type of forest ecosystem found in regions with moderate temperatures and ample rainfall. These forests are characterized by their mixture of deciduous and evergreen trees, as well as a diverse array of plant and animal species. Temperate forests are found in regions such as the northeastern United States, parts of Europe and Asia, and the southeastern coast of Australia.
Temperate forests are home to a wide variety of plants, including both deciduous and evergreen trees, as well as shrubs, ferns, mosses, and wildflowers. The trees in these forests are typically broad-leaved, and their leaves change color in the fall before shedding for the winter. Temperate forests also have a diverse understory, which is made up of smaller trees, shrubs, and other plants that grow beneath the canopy.
Characteristics of Temperate Forests Habitats
The following are the key characteristics of Temperate forests habitats
TREE SPECIES
Temperate forests are dominated by a variety of tree species, including deciduous species such as oak, maple, beech, and hickory, as well as evergreen species like pine, spruce, and hemlock. These tree species provide habitat and food for a wide variety of animals, including insects, birds, and mammals. The different species of trees in these forests have adapted to the specific environmental conditions found in these regions, such as temperature and rainfall.
SOIL
Temperate forests are typically found on nutrient-rich soils, which support the growth of a wide variety of plants. The forest floor is typically covered with a thick layer of leaf litter and other organic matter, which acts as a natural fertilizer for the trees and other plants growing in these ecosystems. Additionally, the decomposition of this organic matter also releases important nutrients back into the soil, which supports the growth of new plants.
SEASONALITY
Temperate forests are characterized by distinct seasons, with cold winters and warm summers. The trees in these forests have adapted to these seasonal changes by shedding their leaves in the fall, which allows them to conserve energy during the winter months. In the spring, the trees begin to grow new leaves and flowers, which signals the start of the growing season.
WILDLIFE
Temperate forests are home to a wide variety of wildlife, including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Some of the most common mammals found in these forests include deer, bears, raccoons, and foxes. Birds such as woodpeckers, owls, and warblers are also commonly found in temperate forests, as are reptiles such as snakes and salamanders.
CONSERVATION
Temperate forests, like other ecosystems, are facing many challenges, including deforestation and fragmentation. Conservation initiatives aim to protect and restore these habitats, through reforestation projects, conservation corridors, and sustainable management of resources. Additionally, efforts to reduce pollution and climate change can help to maintain the health of these ecosystems.
| Characteristics of Temperate Forests Habitats | Description |
|---|---|
| Tree species | Dominated by a variety of deciduous and evergreen tree species, such as oak, maple, beech, hickory, pine, spruce, and hemlock. |
| Soil | Found on nutrient-rich soils, which support the growth of a wide variety of plants. |
| Seasonality | Characterized by distinct seasons, with cold winters and warm summers, and trees adapt to it by shedding leaves and regrowing |
| Wildlife | Home to a wide variety of wildlife, including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. |
| Conservation | Protected and restored through conservation initiatives such as creating protected areas, reforestation projects, and sustainable use of resources. |
Types of Temperate Forests
There are several different types of temperate forests, each with its own unique characteristics and plant species. Some of the most common types of temperate forests include:
Temperate Deciduous Forest
Temperate deciduous forests are found in regions with moderate temperatures and ample rainfall, typically in areas with four distinct seasons. These forests are characterized by their mixture of deciduous trees, which shed their leaves in the fall, and a diverse array of plant and animal species. Some common tree species found in temperate deciduous forests include oak, maple, beech, and hickory.
Temperate Rainforest
Temperate rainforests are found in regions with high rainfall and moderate temperatures. These forests are characterized by their dense canopy of evergreen trees, such as Sitka spruce and western hemlock. The forest floor is typically mossy, and it’s home for other unique plants, and it’s also home for diverse wildlife. These forests are found in regions such as the Pacific Northwest of North America and southwestern South America.
Temperate Coniferous Forest
Temperate coniferous forests are found in regions with moderate temperatures and moderate to high rainfall. These forests are dominated by evergreen coniferous trees such as pine, spruce, and fir, which can be found in parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. They also host a diverse array of understory plants, shrubs and other tree species, and are home to many animal species.
Mediterranean Forest
Mediterranean forests are found in regions with a Mediterranean climate, characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. These forests are characterized by their mixture of evergreen and deciduous trees, such as oak, laurel, and pine. Mediterranean forests are found in regions such as California and the Mediterranean basin.
| Types of Temperate Forests | Characteristics | Common Tree Species |
|---|---|---|
| Temperate Deciduous Forest | Moderate temperatures, ample rainfall, four distinct seasons, mixture of deciduous trees and diverse plant and animal species | Oak, maple, beech, hickory |
| Temperate Rainforest | High rainfall, moderate temperatures, dense canopy of evergreen trees, mossy forest floor | Sitka spruce, western hemlock |
| Temperate Coniferous Forest | Moderate temperatures, moderate to high rainfall, dominated by evergreen coniferous trees | Pine, spruce, fir |
| Mediterranean Forest | Mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, mixture of evergreen and deciduous trees | Oak, laurel, pine |
Each type of temperate forest has its own unique characteristics and plant species, reflecting the different environmental conditions found in these regions. Additionally, it’s worth mentioning that temperate forests are part of a larger, interconnected network of ecosystems, and it’s important to understand their interactions and connections to maintain their health and biodiversity.
Unique Characteristics of Temperate Forest Plants
Temperate forests are home to a wide variety of plants, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the unique characteristics of temperate forest plants include:
| Unique Characteristics of temperate Forest Plants | Description |
|---|---|
| Deciduous and evergreen species | Adaptation to the specific environmental conditions such as temperature and rainfall. |
| Adaptation to seasonal changes | Mechanisms to survive harsh winter conditions, and adaptation to dormant periods |
| Reproduction | Unique reproductive strategies such as producing large quantities of small seeds or seeds dispersed by animals. |
| Leaf and stem adaptations | Broad leaves to maximize surface area for photosynthesis, specialized stem structures such as thorns or toxins to deter herbivores. |
| Mycorrhizal associations | Mutualistic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi to acquire nutrients from the soil |
| Endemism | Endemic to a specific region or habitat, adapted to the unique conditions found in their local environment. |
Deciduous and evergreen species
Temperate forests contain a mixture of deciduous and evergreen tree species, which have adapted to the specific environmental conditions found in these regions, such as temperature and rainfall. Deciduous trees lose their leaves in the fall and regrow them in the spring, which allows them to conserve energy during the winter months. Evergreen trees keep their leaves year-round, which allows them to photosynthesize and survive in cold climates.
Adaptation to seasonal changes
Temperate forest plants have adapted to the seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation patterns. Trees have mechanisms to survive in harsh winter conditions and understory plants have adaptations such as dormancy, and the ability to store energy during the growing season to survive through dormant period.
Reproduction
Many temperate forest plants have unique reproductive strategies, such as producing large quantities of small seeds, or producing seeds that are dispersed by animals. This helps to ensure the survival of the species in the event of a forest fire or other disturbance.
Leaf and stem adaptations
Many temperate forest plants have broad leaves to maximize surface area for photosynthesis, some species have smaller leaves and more compact structure to reduce water loss during hot and dry periods. Some plants also have specialized stem structures such as thorns or toxins to deter herbivores.
Mycorrhizal associations
Many temperate forest plants have a mutualistic relationship with mycorrhizal fungi, which help them to acquire nutrients from the soil, especially phosphorous.
Endemism
Some species of temperate forest plants are endemic, meaning they are only found in a specific region or habitat. These species have adapted to the unique conditions found in their local environment and are often found nowhere else in the world. For example, certain species of ferns or mosses are only found in specific areas of the temperate rainforest.
These unique characteristics of temperate forest plants play an important role in maintaining the diversity and health of these ecosystems. They also provide important resources for wildlife and humans alike.
It’s worth noting that preserving and protecting temperate forests is essential for maintaining the biodiversity and unique characteristics of these plants. By implementing conservation and sustainable use of resources, we can ensure that these important ecosystems remain healthy for generations to come.
Importance of Temperate Forests
Temperate forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, and play a vital role in maintaining the health of the planet. Some of the most important benefits of temperate forests include:
| Importance of temperate Forests | Description |
|---|---|
| Biodiversity | Temperate forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, which support a diverse array of species, from large mammals such as bears and deer to smaller creatures such as birds, reptiles, and insects. |
| Climate Regulation | Temperate forests play a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. They absorb and store large amounts of carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. They also help to maintain the water cycle by releasing water vapor and transpiring. |
| Economic Value | Temperate forests provide a wide range of economic benefits, including timber, non-timber products and recreation. They also provide important ecosystem services such as air and water purification and carbon sequestration. |
| Recreational and Educational Opportunities | Temperate forests offer a wide range of recreational and educational opportunities for people. These forests provide places for hiking, camping, birdwatching, and other outdoor activities. Additionally, they serve as important outdoor classrooms for students of all ages. |
| Cultural Significance | Many communities around the world have deep cultural connections to temperate forests. These forests are often considered sacred places, and are central to the traditional beliefs, values, and practices of these communities. Preserving these forests is essential for maintaining the cultural heritage and identity of these communities. |
Biodiversity
Temperate forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else in the world. These forests support a diverse array of species, from large mammals such as bears and deer to smaller creatures such as birds, reptiles, and insects. This biodiversity is essential for maintaining the overall health and resilience of the ecosystem.
Climate Regulation
Temperate forests play a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. They absorb and store large amounts of carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. They also help to maintain the water cycle by releasing water vapor and transpiring, which can influence local and regional climate, as well as protecting against natural hazards such as floods and landslides.
Economic Value
Temperate forests provide a wide range of economic benefits, including timber, non-timber products and recreation. In addition, they also provide important ecosystem services such as air and water purification and carbon sequestration, that contribute to global economy.
Recreational and Educational Opportunities
Temperate forests offer a wide range of recreational and educational opportunities for people. These forests provide places for hiking, camping, birdwatching, and other outdoor activities. Additionally, they serve as important outdoor classrooms for students of all ages, providing hands-on opportunities to learn about the natural world.
Cultural Significance
Many communities around the world have deep cultural connections to temperate forests. These forests are often considered sacred places, and are central to the traditional beliefs, values, and practices of these communities. Preserving these forests is essential for maintaining the cultural heritage and identity of these communities.
In conclusion, temperate forests play a vital role in maintaining the health and well-being of the planet, and provide a wide range of benefits to both humans and wildlife. Preservation and protection of these forests is essential for maintaining their biodiversity, regulating the Earth’s climate, providing economic benefits, recreation and educational opportunities and protecting cultural heritage.