Forest Habitat
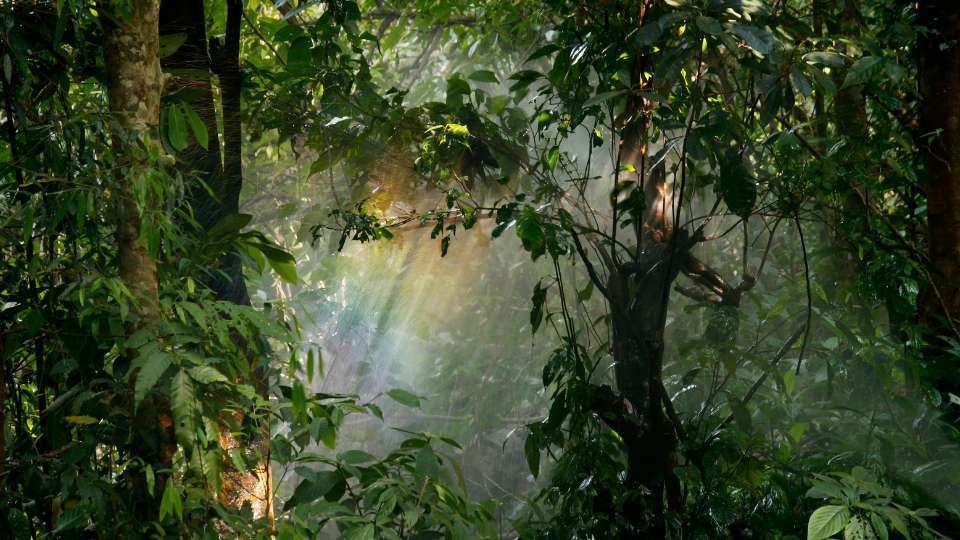

Forests are one of the most diverse habitats for plants, and they can be found in a wide range of climates and regions around the world. Forests are complex ecosystems that support a wide variety of plant and animal species, and they play an important role in maintaining the balance of the planet’s climate and weather patterns. In this article, we will take a closer look at the characteristics of forests as a habitat for plants, and discuss the different types of forests found around the world.
Characteristics of Forest Habitats
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Trees | Forests are characterized by the presence of trees, which are the tallest and most visible plants in a forest and typically the dominant species in terms of biomass and ecological importance. |
| Shrubs, Herbs and mosses | Understory plants, such as shrubs, herbaceous plants, and mosses, grow below the canopy formed by the trees and play an important role in the forest ecosystem by providing food and shelter for animals. |
| Sunlight | The amount of sunlight that reaches the forest floor can vary depending on the density of the canopy, in a dense canopy the forest floor receives very little direct sunlight. |
| Soil Type | Soil type can vary depending on the location of the forest, forests that are located in areas with high precipitation will typically have more nutrient-rich soils and higher levels of moisture. |
| Moisture | The amount of moisture also varies depending on the location of the forest, forests located in dryer regions will have less fertile soils and less moisture. |
Forests are characterized by the presence of trees, shrubs, and herbs, as well as varying levels of sunlight, soil type, and moisture. They are typically categorized by their dominant tree species, such as coniferous forests, which are characterized by the presence of cone-bearing trees, and deciduous forests, which are characterized by the presence of trees that lose their leaves annually.
Forests are home to a wide variety of plant species, including both trees and understory plants. Trees are the tallest and most visible plants in a forest, and they are typically the dominant species in terms of biomass and ecological importance. Understory plants, such as shrubs, herbaceous plants, and mosses, grow below the canopy formed by the trees and play an important role in the forest ecosystem by providing food and shelter for animals.
The amount of sunlight that reaches the forest floor can vary depending on the density of the canopy. In a dense canopy, the forest floor receives very little direct sunlight, and understory plants have adapted to thrive in low-light conditions. In a more open canopy, the forest floor receives more sunlight and supports a greater diversity of plant species.
Soil type and moisture also vary depending on the location of the forest. Forests that are located in areas with high precipitation will typically have more nutrient-rich soils and higher levels of moisture, while those in dryer regions will have less fertile soils and less moisture. This variation in soil and moisture levels can greatly affect the types of plants that can survive and thrive in a given forest ecosystem.
Types of Forests
Forests can be divided into several different types based on their geographic location and the dominant tree species. Some common types of forests include:
Tropical Forests
Tropical forests are found near the equator and are characterized by high temperatures and high levels of precipitation. They are home to a wide variety of plant species, including tall, broad-leaved evergreen trees, as well as smaller shrubs, herbs, and vines. Some examples of tropical forest plants include the mahogany tree, the orchid, and the banana plant.
Temperate Forests
Temperate forests are found in regions with moderate temperatures and moderate levels of precipitation. They are characterized by the presence of deciduous trees, such as oaks, maples, and elms, as well as a variety of understory plants. Some examples of temperate forest plants include the American beech, the trillium and the Redwood tree.
Boreal Forests
Boreal forests, also known as taiga, are found in the northern hemisphere and are characterized by the presence of coniferous trees, such as pines, firs, and spruces. They are typically found in regions with low temperatures and low levels of precipitation. Some examples of boreal forest plants include the white spruce, the Labrador tea and the cranberries.
Montane Forests
Montane forests are found in mountainous regions and are characterized by a wide variety of tree species that are adapted to the specific conditions of high altitude, such as lower temperatures and lower levels of oxygen. Some examples of montane forest plants include the Douglas fir, the quaking aspen, and the Lodgepole pine. These trees are able to survive in the harsh conditions of high altitude by having shorter height and thicker leaves to deal with wind, snow, and cold temperatures. The understory of montane forests is also diverse, with a variety of shrubs, ferns, mosses, and wildflowers that are adapted to the specific conditions of high altitude.
| Type of Forest | Characteristics | Examples of Trees and Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical Forests | high temperatures, high levels of precipitation, tall, broad-leaved evergreen trees, shrubs, herbs, and vines | Mahogany, Orchid, Banana plant |
| Temperate Forests | moderate temperatures, moderate levels of precipitation, deciduous trees (oaks, maples, and elms) and understory plants | American Beech, Trillium, Redwood |
| Boreal Forests | low temperatures, low levels of precipitation, coniferous trees (pines, firs, and spruces) | White spruce, Labrador Tea, Cranberries |
| Montane Forests | high altitude, shorter trees, thicker leaves, diverse understory | Douglas fir, Quaking aspen, Lodgepole pine, ferns, mosses, wildflowers |
Ecological Importance of Forests
Forests play an important role in maintaining the balance of the planet’s climate and weather patterns. They help to regulate the water cycle, by absorbing and releasing large quantities of water, which in turn can help to mitigate the effects of drought and flooding. They also act as carbon sinks, absorbing large quantities of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Forests are also important for biodiversity, they are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. They also provide essential ecosystem services such as pollination, seed dispersal, soil stabilization, and pest control.
Forests also play an important role in human life. They are a source of food, medicine, and building materials for many indigenous communities around the world. Forests also provide recreational opportunities such as hiking, camping, and hunting.
| Ecological Importance | Description |
|---|---|
| Climate and Weather regulation | Forests help to regulate the water cycle, by absorbing and releasing large quantities of water, which in turn can help to mitigate the effects of drought and flooding. They also act as carbon sinks, absorbing large quantities of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. |
| Biodiversity | Forests are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. They also provide essential ecosystem services such as pollination, seed dispersal, soil stabilization, and pest control. |
| Human benefits | Forests provide a source of food, medicine, and building materials for many indigenous communities around the world. They also provide recreational opportunities such as hiking, camping, and hunting. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, forests are complex ecosystems that support a wide variety of plant and animal species. They play an important role in maintaining the balance of the planet’s climate and weather patterns and are vital for human survival and well-being. Understanding the characteristics and types of forests, as well as their ecological importance, can help us to better understand and appreciate the diversity of plant life on our planet and take steps to protect and preserve these vital habitats.